Scientists Are Using New Satellite Tech to Find Glow-in-the-Dark Milky Seas of Maritime Lore

lus69/istockphoto.com
For centuries, sailors have told tales of huge swaths of ocean glowing on dark nights.
“The whole appearance of the ocean was like a plain covered with snow. There was scarce a cloud in the heavens, yet the sky … appeared as black as if a storm was raging. The scene was one of awful grandeur, the sea having turned to phosphorus, and the heavens being hung in blackness, and the stars going out, seemed to indicate that all nature was preparing for that last grand conflagration which we are taught to believe is to annihilate this material world.”
– Captain Kingman of the American clipper ship Shooting Star, offshore of Java, Indonesia, 1854
For centuries, sailors have been reporting strange encounters like the one above. These events are called milky seas. They are a rare nocturnal phenomenon in which the ocean’s surface emits a steady bright glow. They can cover thousands of square miles and, thanks to the colorful accounts of 19th-century mariners like Capt. Kingman, milky seas are a well-known part of maritime folklore. But because of their remote and elusive nature, they are extremely difficult to study and so remain more a part of that folklore than of science.
I’m a professor of atmospheric science specializing in satellites used to study Earth. Via a stat-of-the-art generation of satellites, my colleagues and I have developed a new way to detect milky seas. Using this technique, we aim to learn about these luminous waters remotely and guide research vessels to them so that we can begin to reconcile the surreal tales with scientific understanding.
Sailors' tales
To date, only one research vessel has ever encountered a milky sea. That crew collected samples and found a strain of luminous bacteria called Vibrio harveyi colonizing algae at the water’s surface.
Unlike bioluminescence that happens close to shore, where small organisms called dinoflagellates flash brilliantly when disturbed, luminous bacteria work in an entirely different way. Once their population gets large enough – about 100 million individual cells per milliliter of water – a sort of internal biological switch is flipped and they all start glowing steadily.
Luminous bacteria cause the particles they colonize to glow. Researchers think the purpose of this glow could be to attract fish that eat them. These bacteria thrive in the guts of fishes, so when their populations get too big for their main food supply, a fish’s stomach makes a great second option. In fact, if you go into a refrigerated fish locker and turn off the light, you may notice that some fish emit a greenish-blue glow – this is bacterial light.
Now imagine if a gargantuan number of bacteria, spread across a huge area of open ocean, all started glowing simultaneously. That makes a milky sea.
While biologists know a lot about these bacteria, what causes these massive displays remains a mystery. If bacteria growing on algae were the main cause of milky seas, they’d be happening all over the place, all the time. Yet, per surface reports, only about two or three milky seas occur per year worldwide, mostly in the waters of the northwest Indian Ocean and off the coast of Indonesia.
Satellite solutions
If scientists want to learn more about milky seas, they need to get to one while it’s happening. Trouble is, milky seas are so elusive that it has been almost impossible to sample them. This is where my research comes into play.
Satellites offer a practical way to monitor the vast oceans, but it takes a special instrument able to detect light around 100 million times fainter than daylight. My colleagues and I first explored the potential of satellites in 2004 when we used U.S. defense satellite imagery to confirm a milky sea that a British merchant vessel, the SS Lima, reported in 1995. But the images from these satellites were very noisy, and there was no way we could use them as a search tool.
We had to wait for a better instrument – the Day/Night Band – planned for the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s new constellation of satellites. The new sensor went live in late 2011, but our hopes were initially dashed when we realized the Day/Night Band’s high sensitivity also detected light emitted by air molecules. It took years of studying Day/Night Band imagery to be able to interpret what we were seeing.
Finally, on a clear moonless night in early 2018, an odd swoosh-shaped feature appeared in the Day/Night Band imagery offshore Somalia. We compared it with images from the nights before and after. While the clouds and airglow features changed, the swoosh remained. We had found a milky sea! And now we knew how to look for them.
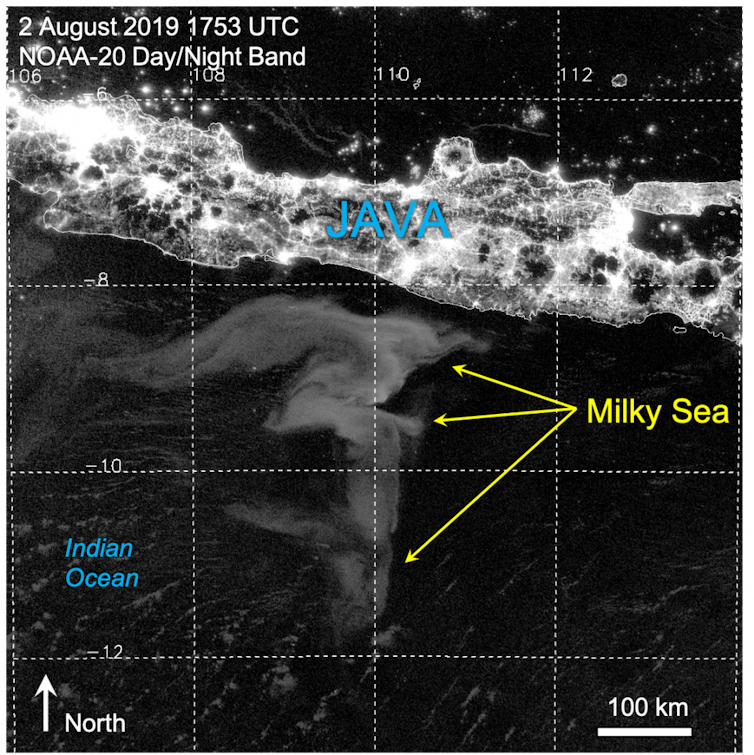
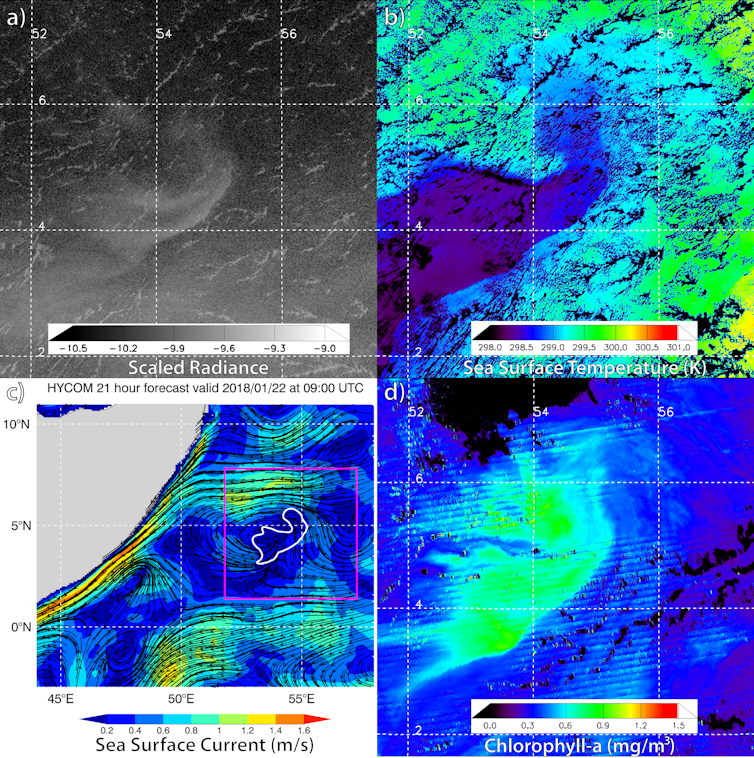
The “aha!” moment that unveiled the full potential of the Day/Night Band came in 2019. I was browsing the imagery looking for clouds masquerading as milky seas when I stumbled upon an astounding event south of the island of Java. I was looking at an enormous swirl of glowing ocean that spanned over 40,000 square miles (100,000 square km) – roughly the size of Kentucky. The imagery from the new sensors provided a level of detail and clarity that I hadn’t imagined possible. I watched in amazement as the glow slowly drifted and morphed with the ocean currents.
We learned a lot from this watershed case: how milky seas are related to sea surface temperature, biomass and the currents – important clues to understanding their formation. As for the estimated number of bacteria involved? Approximately 100 billion trillion cells – nearly the total estimated number of stars in the observable universe!
The future is bright
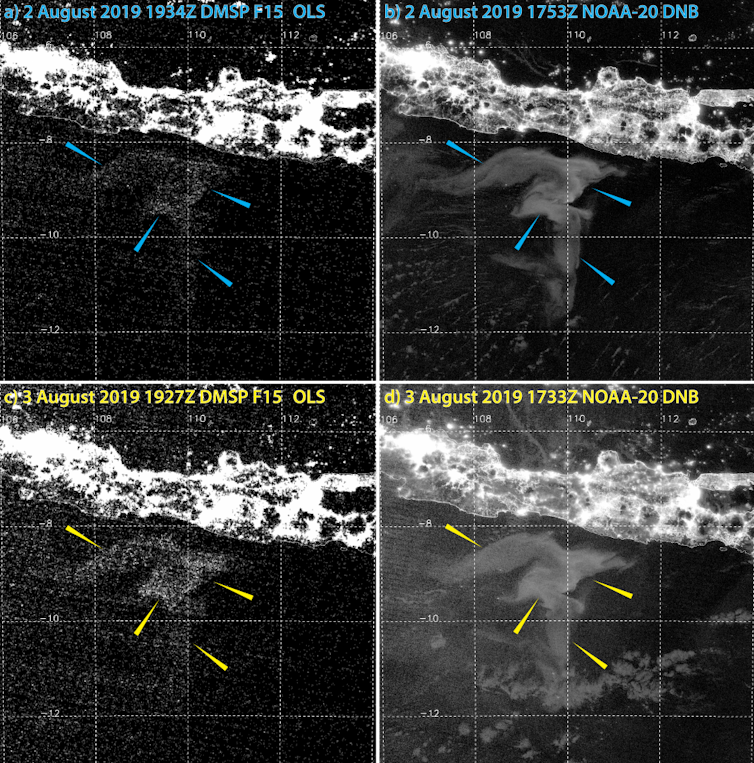
Compared with the old technology, viewing Day/Night Band imagery is like putting on glasses for the first time. My colleagues and I have analyzed thousands of images taken since 2013, and we’ve uncovered 12 milky seas so far. Most happened in the very same waters where mariners have been reporting them for centuries.
Perhaps the most practical revelation is how long a milky sea can last. While some last only a few days, the one near Java carried on for over a month. That means that there is a chance to deploy research craft to these remote events while they are happening. That would allow scientists to measure them in ways that reveal their full composition, how they form, why they’re so rare and what their ecological significance is in nature.
If, like Capt. Kingman, I ever do find myself standing on a ship’s deck, casting a shadow toward the heavens, I’m diving in!
Steven D. Miller is a professor of atmospheric science at Colorado State University.
![]() This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.





