2022’s Billion-dollar Disasters: Climate Change Helped Make it US’s 3rd Most Expensive Year on Record

3D Render of a Topographic Map of the Caribbean Sea with the clouds from September 26, 2022. Major Hurricane Ian approaching Western Cuba. All source data is in the public domain. Cloud texture: Global Imagery Browse Services (GIBS) courtesy of NASA, GOES data courtesy of NOAA. FrankRamspott/istockphoto
Climate change seems to be making natural disasters more expensive.
U.S. weather disasters are getting costlier as more people move into vulnerable areas and climate change raises the risks of extreme heat and rainfall, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration officials warned as they released their annual billion-dollar disasters report on Jan. 10, 2023.
Even with an average hurricane season, 2022 had the third-highest number of billion-dollar disasters in the U.S. since 1980.
In all, there were 18 disasters that each caused more than US$1 billion in damage in the U.S. The list included three hurricanes, two tornado outbreaks, a destructive fire season, several extreme storms and a drought that disrupted sectors across the economy.
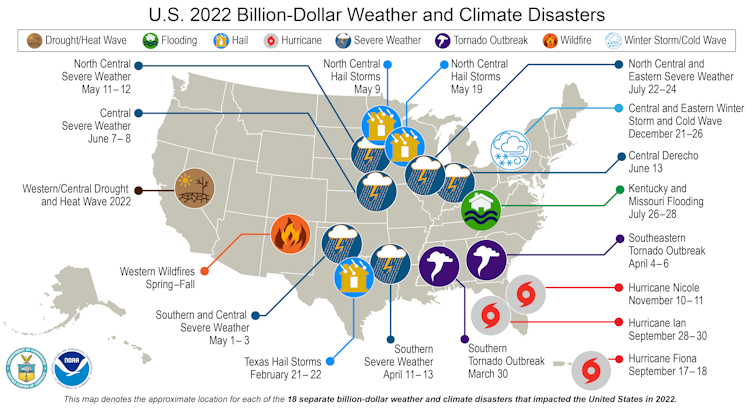
It was also the third-costliest year, with past years adjusted for inflation, due primarily to Hurricane Ian’s widespread damage in Florida. Together, the 2022 disasters topped $165 billion, with damage still being tallied from December’s winter storms.
Several scientists wrote about the year’s U.S. weather disasters and connections to climate change. Here are three essential reads from The Conversation’s archive:
1. Hurricane Ian
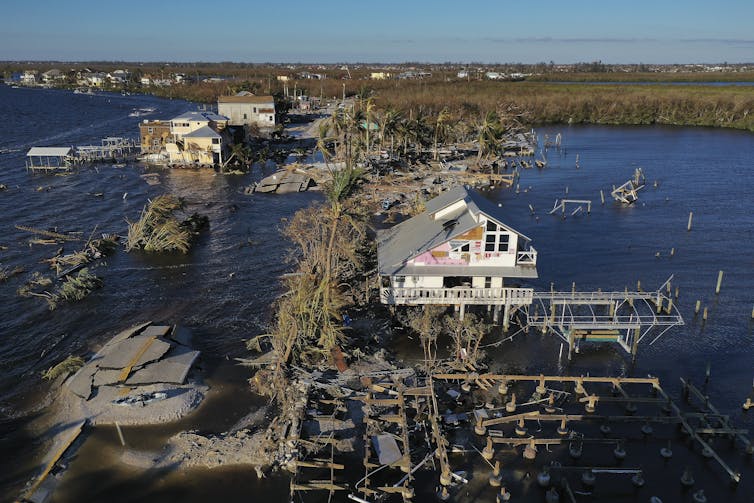
The most expensive U.S. weather disaster of 2022 was Hurricane Ian, which grew into a monster of a storm over the warm waters of the Gulf of Mexico in late September.
Ian hit the barriers islands off Fort Myers, Florida, with 150-mph winds, tying for the fifth-strongest wind speed at U.S. landfall on record. Its storm surge swept through coastal neighborhoods, where the population has boomed in recent years, and its rainfall caused flooding across a large swath of the state. Twenty inches of rain fell in Daytona Beach, triggering erosion, with devastating consequences.
At least 144 deaths were attributed to the storm in Florida alone, and the total damage neared $113 billion.

Did global warming play a role?
In some ways, yes, but there are still a lot of unknowns when it comes to hurricanes, explained climate scientists Matthew Barlow of UMass-Lowell and Suzana Camargo of Columbia University.
For example, “it is clear that climate change increases the upper limit on hurricane strength and rain rate, and that it also raises the average sea level and therefore storm surge,” Barlow and Camargo wrote.
Less clear is global warming’s influence on hurricane frequency, though research points to an uptick in the strength of storms that do form. “We expect more of them to be major storms,” the scientists wrote. “Hurricane Ian and other recent storms, including the 2020 Atlantic season, provide a picture of what that can look like.”
Globally, 2022 was the fifth or sixth warmest year in over 140 years of record-keeping, according to data sets from NASA and NOAA. The last eight years have been the warmest on record. Ocean temperatures were also at record highs in 2022.
2. The drought
The second-costliest disaster, at over $22 billion, was the widespread drought across much of the U.S. West and parts of the Midwest. It left reservoirs near record lows, disrupted farming in several states and temporarily shut down barge traffic on the Mississippi River.
At one point, 2,000 barges were backed up along the river, where 92% of U.S. agriculture exports travel.
Rivers the size of the Mississippi can be slow to respond to droughts, but during the flash drought of 2022, the river fell 20 feet in less than three months – even though its major tributaries were flowing at normal levels, wrote earth scientists Ray Lombardi, Angela Antipova and Dorian Burnette of the University of Memphis.
They described the dramatic drop in the river’s water levels as a “preview of a climate-altered future.”
“Warmer atmospheric temperatures have the potential to evaporate more water, causing drought, and to hold more water, causing extreme rainfall,” the scientists wrote. “Over the past 100 years, year-to-year changes from very dry to very wet in the Mississippi River Valley have become more frequent. We expect this trend to continue as global temperatures continue to rise because of climate change.”
3. Extreme storms and flooding
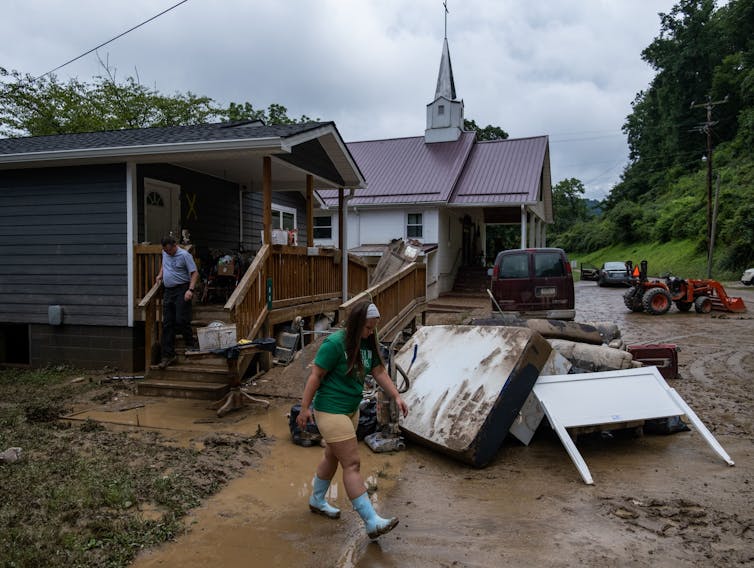

Many of 2022’s billion-dollar disasters involved extreme storms, including hail, deadly tornado outbreaks, and a derecho that damaged property from Wisconsin to West Virginia.
It was also a summer of flooding, beginning with rain falling on snow that turned the Yellowstone River into a record-shattering torrent. St. Louis, Dallas, eastern Kentucky, southern Illinois and Death Valley were all hit with 1,000-year floods. Storms in the South knocked out Jackson, Mississippi’s fragile water supply for weeks.
Climate models have consistently shown that extreme rainfall events will become more common as the climate warms, wrote University of Dayton climate scientist Shuang-Ye Wu.
Some of that is basic physics – warmer air increases the amount of moisture that the atmosphere can hold by about 7% per degree Celsius. Increased humidity can enhance latent heat in storms, increasing their intensity and leading to heavier rainfall, Wu explained.
Even though humans are becoming more adept at managing climate risks, research published in 2022 found that extreme flooding and droughts are still getting deadlier and more expensive, and the costs are likely to continue to rise.
“This past summer might just provide a glimpse of our near future as these extreme climate events become more frequent,” Wu wrote. “To say this is the new ‘normal,’ though, is misleading. It suggests that we have reached a new stable state, and that is far from the truth.”
This article was updated with NOAA’s release of global temperature data on Jan. 12, 2023. It is a roundup of articles from The Conversation’s archives.
![]()
Stacy Morford, Environment + Climate Editor, The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.





