The Algorithm That Makes Preschoolers Obsessed With YouTube

Grisha Bruev/Shutterstock.com
Surprise eggs and slime are at the center of an online realm that’s changing the way the experts think about human development.
Toddlers crave power. Too bad for them, they have none. Hence the tantrums and absurd demands. (No, I want this banana, not that one, which looks identical in every way but which you just started peeling and is therefore worthless to me now.)
They just want to be in charge! This desire for autonomy clarifies so much about the behavior of a very small human. It also begins to explain the popularity of YouTube among toddlers and preschoolers, several development psychologists told me.
If you don’t have a 3-year-old in your life, you may not be aware of YouTube Kids, an app that’s essentially a stripped-down version of the original video blogging site, with videos filtered by the target audience’s age. And because the mobile app is designed for use on a phone or tablet, kids can tap their way across a digital ecosystem populated by countless videos—all conceived with them in mind.
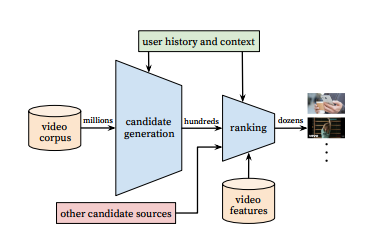
The videos that surface on the app are generated by YouTube’s recommendation algorithm, which takes into account a user’s search history, viewing history, demographic region, gender, age, and other individual data. The algorithm is basically a funnel through which every YouTube video is poured—with only a few making it onto a person’s screen.
This recommendation engine poses a difficult task, simply because of the scale of the platform. “YouTube recommendations are responsible for helping more than a billion users discover personalized content from an ever-growing corpus of videos,” researchers at Google, which owns YouTube, wrote in a 2016 paper about the algorithm. That includes many hours of video uploaded to the site every second of every day. Making a recommendation system that’s worthwhile is “extremely challenging,” they wrote, because the algorithm has to continuously sift through a mind-boggling trove of content and instantly identify the freshest and most relevant videos—all while knowing how to ignore the noise.
And here’s where the ouroboros factor comes in: Kids watch the same kinds of videos over and over. Videomakers take notice of what’s most popular, then mimic it, hoping that kids will click on their stuff. When they do, YouTube’s algorithm takes notice, and recommends those videos to kids. Kids keep clicking on them, and keep being offered more of the same. Which means video makers keep making those kinds of videos—hoping kids will click.
This is, in essence, how all algorithms work. It’s how filter bubbles are made. A little bit of computer code tracks what you find engaging—what sorts of videos do you watch most often, and for the longest periods of time?—then sends you more of that kind of stuff. Viewed a certain way, YouTube Kids is offering programming that’s very specifically tailored to what children want to see. Kids are actually selecting it themselves, right down to the second they lose interest and choose to tap on something else. The YouTube app, in other words, is a giant reflection of what kids want. In this way, it opens a special kind of window into a child’s psyche.
But what does it reveal?
“Up until very recently, surprisingly few people were looking at this,” says Heather Kirkorian, an assistant professor of human development in the School of Human Ecology at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. “In the last year or so, we’re actually seeing some research into apps and touchscreens. It’s just starting to come out.”
Kids videos are among the most watched content in YouTube history. This video, for example, has been viewed more than 2.3 billion times, according to YouTube’s count:





